Elite Heat Shield
The Elite Heat Shield turns the fire tube into a radiant heat source as opposed to direct flame heat transfer. Reducing the direct flame impingement will significantly enhance the life of the fire tube.
Hot spots or direct flame impingement areas are a direct cause of fire tube failures. Corrosion will seek out areas of difference when attacking carbon steel. Any slight temperature variation in a fire tube increases the chances of corrosion damage exponentially.
One of the more common ways attempted to reduce “hot spots” is to use a heat shield. This shield attempts to provide a layer of protection between the flame and the fire tube. These shields traditionally come in different variations such as thickness and shape and they all are typically made of carbon steel.
We are THE LEADER in fire tube management and failure prevention. The Elite Scanning System has allowed us to measure, track and trend over 12,000 fire tubes (as of 2019). We have documented trends with all of the many variations of fire tube shields.

Basic heat transfer tells us that the types of heating sources used for fire tubes are commonly flawed.
When you are trying to heat one area of a fire tube in hopes to heat the entire vessel, it just does not work well because carbon steel does not disperse heat. When you have fluid on the other side it makes the heat transfer even more challenging.
A misconception is that the thicker the heat shield, the longer the fire tube will last. This is incorrect because the thicker the steel, the more heat is required to heat the vessel. In turn, this will create hot spots in the areas not covered by the shield.
Something else that is often overlooked is a phenomenon called "stack effect". Simply stated, the colder it is outside and the taller the exhaust stack, the more heat is flowing out of the top of the fire tube stack. This can equate to thousands of cubic feet per minute of air, and is like trying to heat your home with all of the windows open.
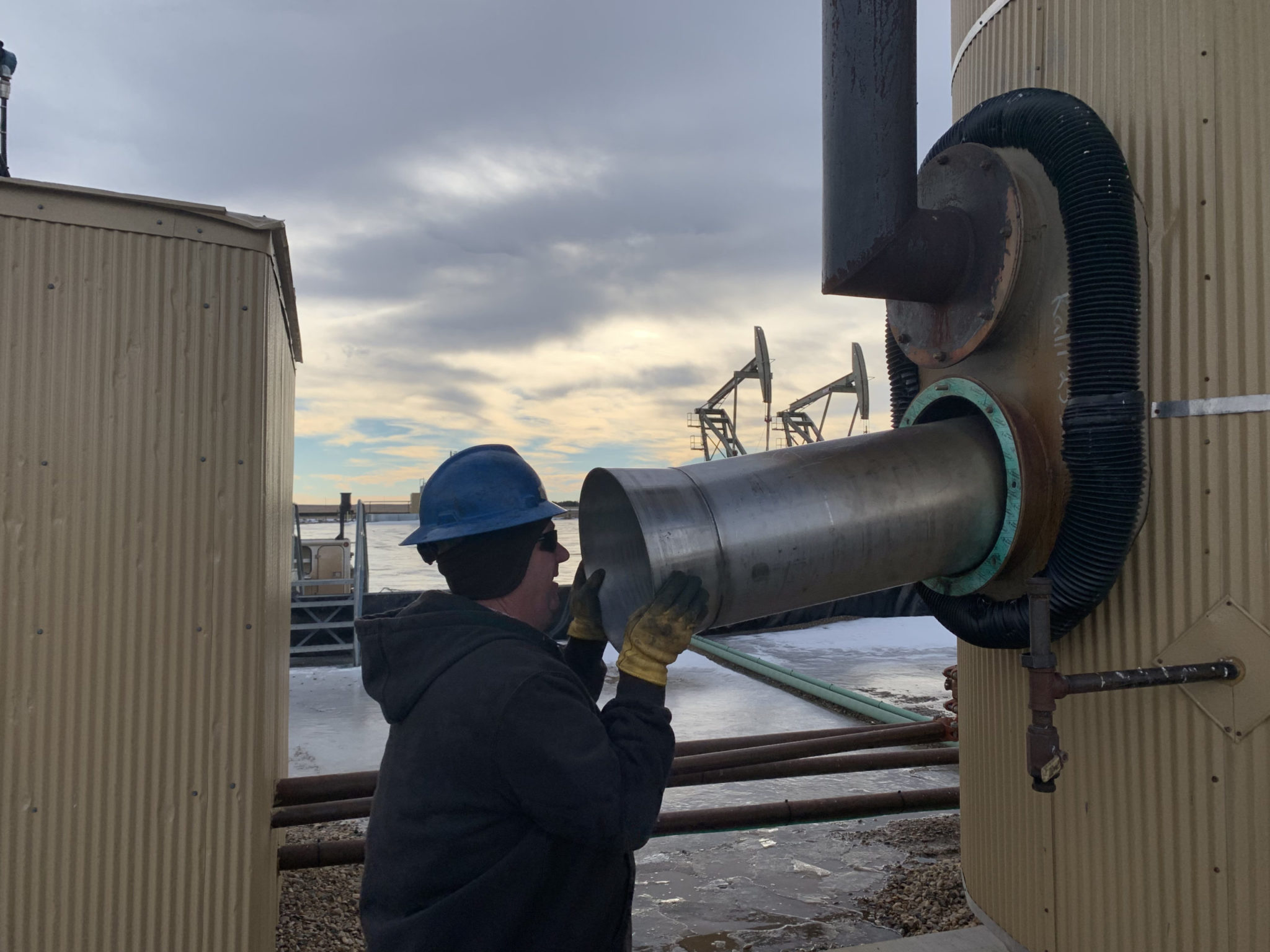
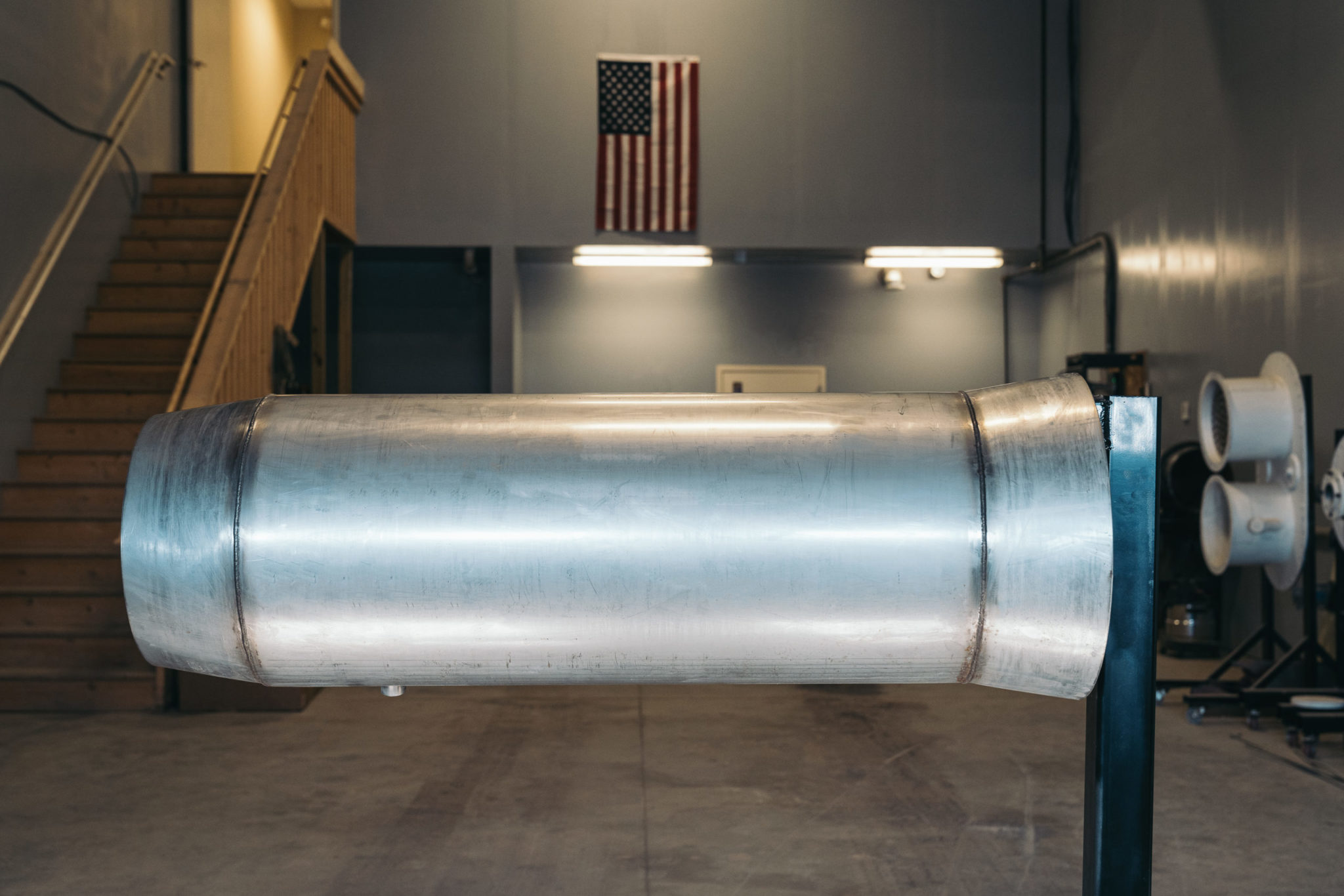
Elite Energy took on the task of developing a heat shield that addressed all of the factors. What we have produced is a revolutionary approach to fire tube heat shields. We have turned the heating mechanism from a direct heat system to a radiating heat system. This is the same theory behind modern day boilers.
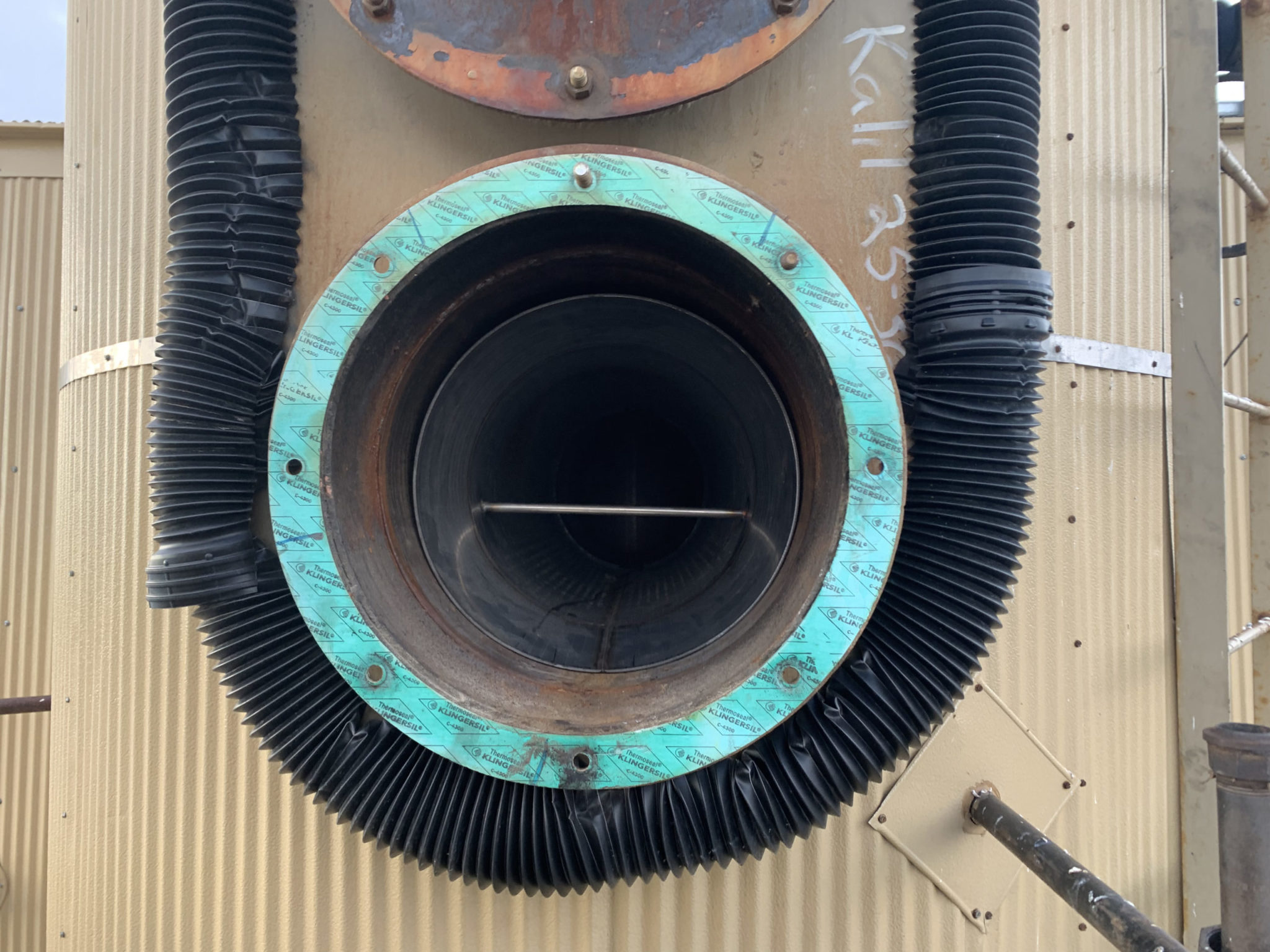
The shield is made of a high heat, high grade stainless steel. It is designed to withstand 1400-degree temperature. It is thin enough to not interfere with the transfer, but yet durable enough to last the life of the treater.
Average Heat Shield
- Made out of carbon steel and does not allow proper heat distribution.
- Allows airflow around the outside of the shield, wasting energy to make up for the lost heat.
Elite Heat Shield
- Uses high quality, stainless steel that allows the proper distribution of heat.
- Funnels air flow into the center of the tube, allowing more concentrated oxygen and resulting in a more effective flame.
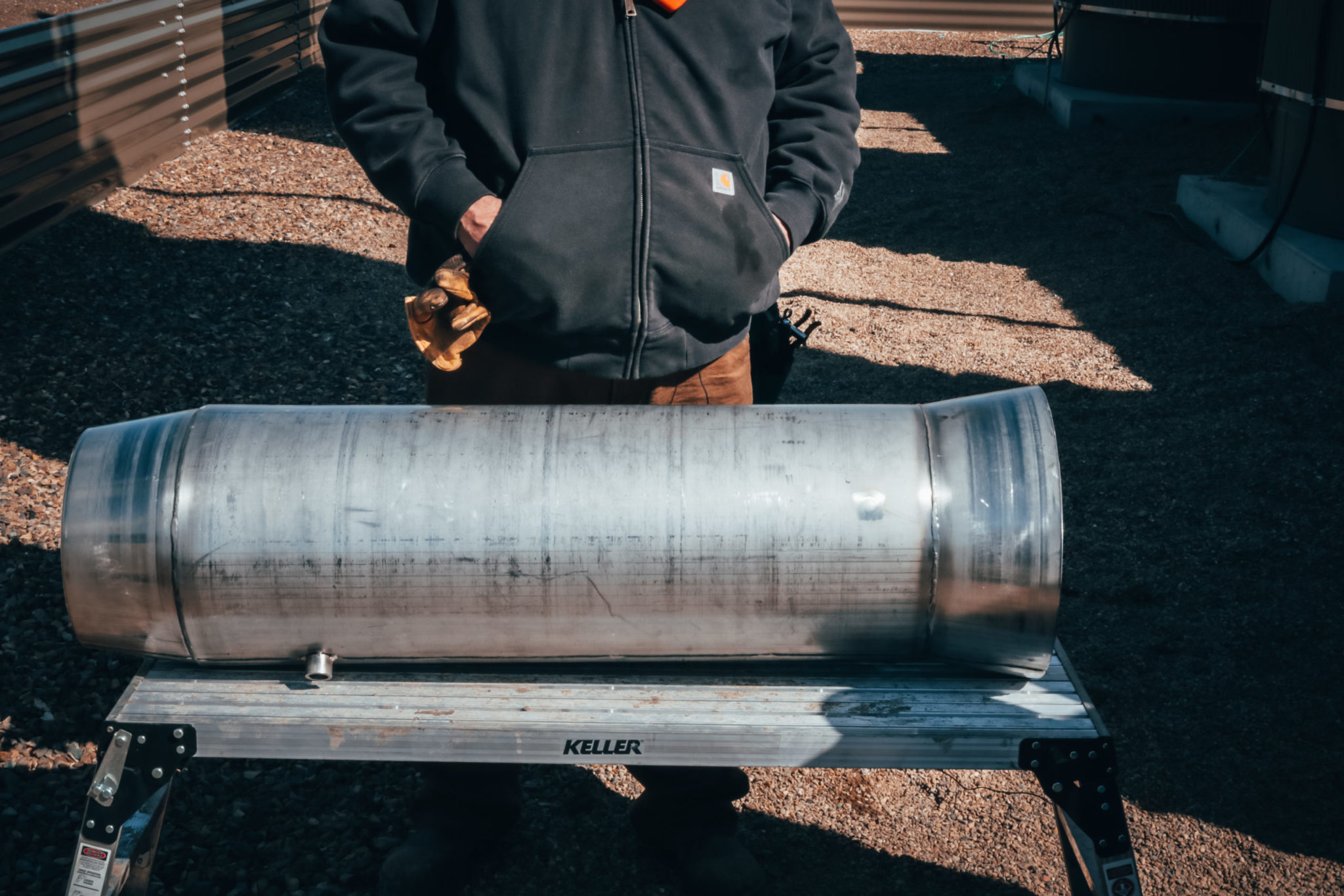

Stainless steel was chosen because of its superb heat distribution qualities. The commercial grade cookware is made of stainless steel because it will distribute heat evenly and has no “hot spots”.
The shape of the fire tube is the most revolutionary part of the heat shield. The concept was taken from a jet engine design. The front part of the shield devotes all of the air flow towards the center of the shield thus, preventing hot or cold air to pass through the fire tube at high speeds.
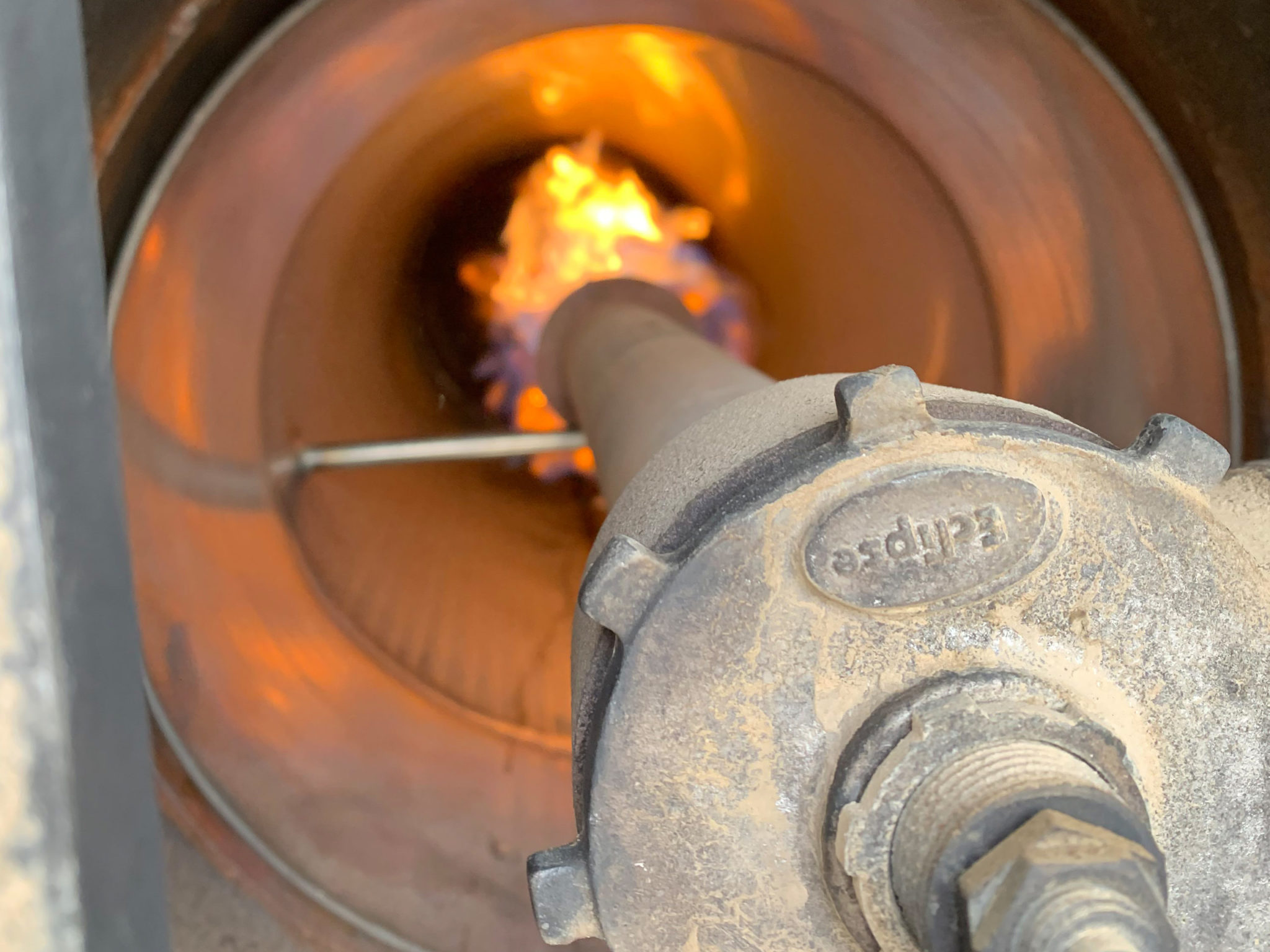
When the air is funneled to the center, it enters into the heat chamber. This accomplishes a few objectives; it adds more concentrated oxygen to the burner, increasing the heat and reducing the unburned carbon. It produces a more effective flame. And it also causes the air to slow down which means the heat stays in the fire tube longer, increasing the heat exchange process.
The shield also has a centering bar. This will keep the burner centered at all times. No further need for burner stands because this will not allow the burner to tip and overheat any portion of the fire tube.
This shield is a revolutionary leap in fire tube management which will increase the service life of all heater treater tubes.